- Features
- Features
- Searchable Fields
- Libraries
- Facet Features
- Types of Facets
- Configure Facets
- Field Mapping
- Field Properties
- Configure Site
- Profile
- Team Management
- Sites
- Global Coverage
- Disaster Recovery
- Features
- Template Selection
- Keyword Suggestions
- In-Field Suggestions
- Top Search Queries
- Popular Products
- Trending Queries
- Promoted/Blacklisted Suggestions
- Real-time Preview
- Instantaneous Publishing
- Ranking Insights
- Clickstream Data
- Boost/Bury
- Sort
- Slot
- Pin
- Filter
- Landing Pages
- Redirects
- Set Banners
- Ranking Insights
- Create a Site Rule
- Managing Field Rules
- Managing Query Rules
- Campaign
- A top-down approach
- Faster and simpler
- Relevant Metrics for better analysis
- Interactive and easy-to-view preview
- Feature-filled Listing Page
- Promotions
- Banners
- Facets
- Redirects
- Add New Promotions
- Boost/Bury
- Sort
- Slot
- Pin
- Filter
- Landing Pages
- All Queries
- Query-based Banner
- Field-based Banner
- Creating Field-based Facets
- Create a Site Rule
- Overall Performance
- Query Report
- Zero Result Queries
- Product Reports
- In-field Suggestions
- Keyword Suggestions
- Top Search Queries
- Popular Products
Catalog Management
Catalog management allows you to configure your catalog from the console. You can check the status of your recent catalog uploads, change field mappings to allow our algorithms to understand your catalog better, make changes in certain schema items directly from the console.
Field Mapping
The fields for a product are defined in the schema file with their respective values defined in the feed file. For example, a product “Mobile phone” can have fields like brand, price, color, manufacturing date, etc.
Why do we need to map fields?
You need to map fields because you might have defined the field name differently in your catalog than what exists as Unbxd’s feature field attribute. In such cases, the particular field attribute then becomes unsearchable because of the mismatch.
Suppose, you have called your field ‘amount1’, ‘amount2’, ‘amount3’ in your catalog and you know that ‘amount3’ represents Price. You can use Field mapping to map ‘Price’ to ‘amount3’ so that going forward you can just mention ‘Price’ in any of your campaign and we’ll know to map it to ‘amount3’ field in your catalog.
What are Feature fields and Custom Fields?
Feature Fields are pre-defined Unbxd fields while Custom fields are the fields define by you.
Let’s read about them in detail.
Feature Fields
Feature fields are a list of predefined Unbxd fields with a fixed schema that doesn’t need to be defined in the feed file. These fields are necessary for Autosuggest and Recommendations to work properly.
In most cases, you do not have to define the schema for these fields, however, when the feature field does not match with the corresponding field within your product feed, you can define the schema by the dataType of that field.
For example, if you have the field ‘amount’ that indicates the price of the product, you can map the field ‘amount’ to ‘price’ and not have to redefine the schema.
In another example, if the “size” field in your catalog has data type “decimal” instead of text, the schema for the “size” field has to be defined in the product feed. Similarly, if the “gender” field in your catalog is “multivalue=true” instead of false, the schema for the “gender” field would need to be defined before the product attribute data in the Product Feed.
NOTE: Feature Fields can be used without explicitly defining them in the schema. If you have a similar field, you can either map it to the corresponding feature field from the Console or rename your existing field to a feature field in the schema.
In case you are navigating through the self-serve flow:
Previously all the feature fields were showing up in the console even if they were not present in the catalog. This used to cause confusion e.g. say catalog has field “Price”. Users will see two fields “price” (feature field) and “Price” ( from use catalog ) leading to confusion.
To fix this, the following change was done:
- Only the fields present on the user catalog will be visible to the user. All the feature fields will be hidden by default.
- All the fields present in the user catalog should also be present in the schema upload.
- If a feature field is present in the user catalog,
then it should be present in the schema upload with the same data type as of that feature field. Say “category” is present in the catalog, then it should be added with data type “string” in schema upload. Only after that, this file will show up in the console. - Special case: fields of data type “path” are handled differently. Say field “catinfo” is of data type “path. Along with “catinfo”, “catinfo1”, “catinfo2” etc will also be visible to user.
Custom Fields
Attributes that are not a part of our list of Feature Fields but part of your product catalog are known as Custom Fields. These attributes and their properties are included in your schema.
Like Feature fields, our search engines use these attributes to power product discovery on your web page.
Field Properties
Field properties provides a quick glimpse of the attributes in your catalog and the schema set for the attributes. Each product that you add to the catalog has a number of attributes defining the product like color, brand, size etc. Field properties define the fields in more detail.
Suppose we have a product ‘mobile phone’ for which the fields are defined as color, brand, and manufacturing date. Now, fields like ‘color’ and ‘brand’ can contain multiple values as colors can be red, blue, green and brand can be anything like Apple, Samsung, or so. But the field ‘manufacturing date’ can have just one value as the date cannot contain multiple values. So, field properties are defined in a similar way.
You can view the field properties for products by navigating to Manage > Configure Site > Field Properties.
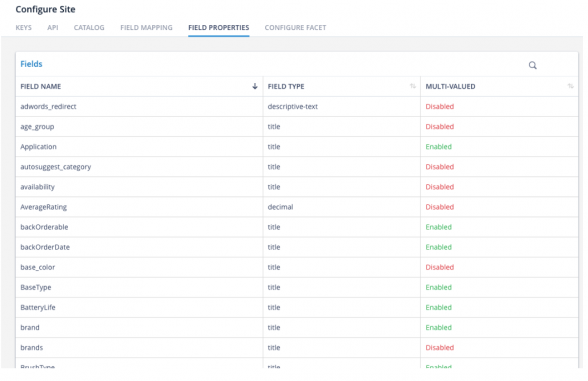
The screen displays:
|
Attributes |
Description |
|
Field Name |
The name of the field in the catalog for a product. Ex. color, brand, price etc. |
|
Field Type |
The value of the field. If it contains a title, a descriptive-text, or a decimal value. |
|
Multi-Valued |
Defines if the field takes in multiple values (Enabled) or not (Disabled). |
- Did this answer your question?
On this Section
- To create a Query Rule
- To Edit a Query Rule
- Delete a Query Rule
- Campaign States
- Create Campaigns
- Edit Campaigns
- Preview Campaigns
- Duplicate Campaigns
- Delete Campaigns